8 Strategies for Scaffolding Instruction
Instructional Coaching, Teaching TipsWith the advent of the common-core standards, our thinking about how to support second language learners has become super important. While opting for services like Translation Services London is an excellent way to get one’s work translated, one also has to know more than one language fluently. Our current focus for supportive instruction may be on grammar and vocabulary or we may be modifying the texts English Language Learners (ELLs) work with during a lesson so they’re at a more “appropriate level.” Under the standards developed through the Common Core State Standards Initiative, however, instruction for ELLs will have to move beyond modifying lesson materials and teaching fundamental components of language. Educators now have to ensure that we are teaching ALL kids, no matter their language background or where they are academically, how to grapple with complex, grade level information and texts.
So how do we do this? Well, a piece of it is thinking more carefully about what supports or scaffolds we can add to our instruction.
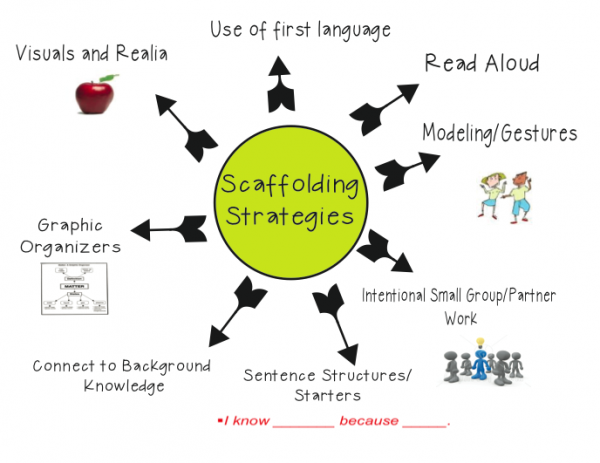
Through my experience working as a classroom teacher in an urban school with a large number of second language learners, along with two years experience as our school’s English Language Acquisition Teacher Leader, I have identified eight “scaffolding strategies” that I believe should always be considered when planning instruction for second language learners:
Click Here for the 8 Scaffolding Strategies Printable
When I set out to plan a lesson, I always consider how to use any or all of these eight scaffolding strategies to support comprehension and language development.
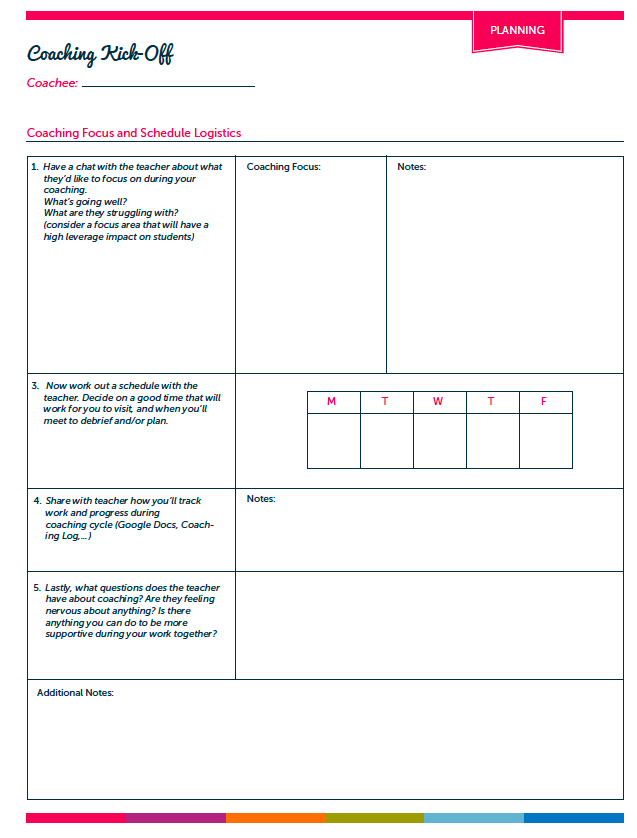
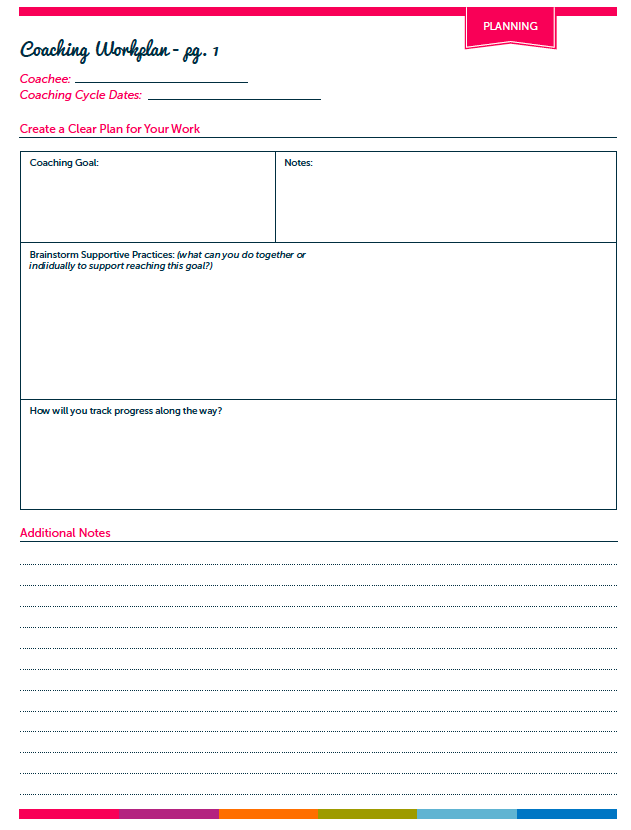
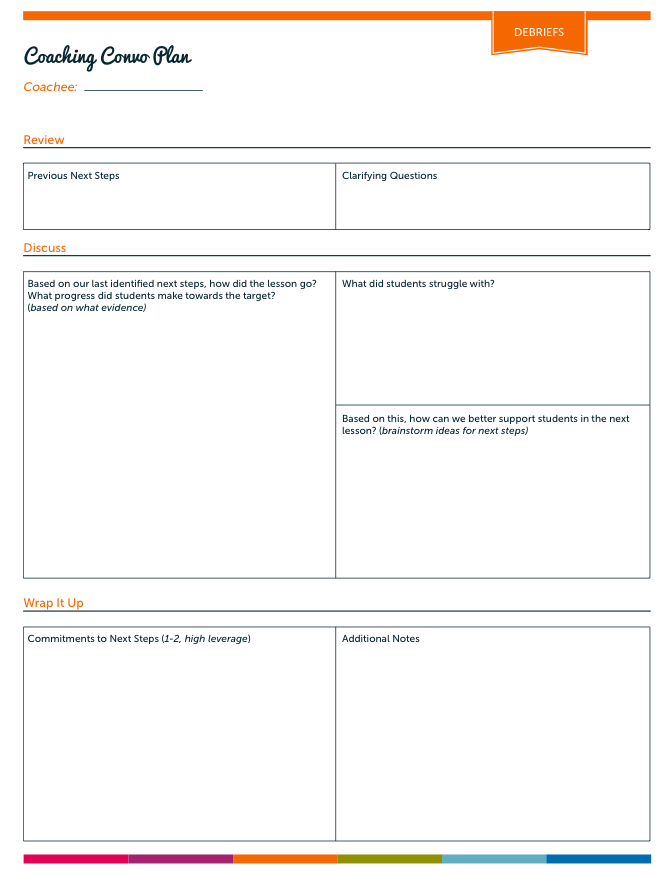
1. Visuals and Realia
Whenever I can I include realia, or real life, tangible objects in my lessons. I have found that realia is super supportive for vocabulary development and engagement. For example, I recently selected a text about coral reefs for a close read lesson. I wasn’t sure students would know what “coral” was, so I brought in an actual piece of coral to pass around. If you don’t have realia available for a lesson, use visuals or images! You can frequently find me on Google images, looking for that just right visual to support my lesson.
2. Modeling/Gestures
If you were to observe me teaching a lesson, you would likely see me making all kinds of funny looking gestures. Funny looking maybe, but supportive definitely! When all you do is talk/lecture to students who don’t speak English as their first language, most of what you say will probably fly right over their head. Modeling and gestures help bring your words to life. Couple this with the use of supportive visuals and say hello to comprehension!
3. Connect to Background Knowledge
When planning for the “hook” or introduction in a lesson, I consider what background knowledge students might have that I can connect to. For example, I might show them a picture of something related to our lesson and ask them a question about it. Connecting previous knowledge/learning to new learning is always a great support for ELLs.
4. Graphic Organizers
Graphic organizers may not be an appropriate scaffold for every lesson, but they are for many! You can create your own or use one of the many free ones to be found on the www. Graphic organizers can be used as a tool to help students organize their thinking when responding to a text. They key is not to make them too complicated or they may end up being exactly the opposite of a useful thinking support.
5. Sentence Structures/Starters
Sentence structures can be a great support for English Language Learners. I often use them during the close of a lesson in the debrief or share. You can also slightly differentiate graphic organizers or recording sheets you provide students by adding sentence structures.
6. Read Aloud
Reading a grade level, complex text aloud to students at the start of the lesson can serve three important purposes: support engagement, support fluency, and give ELLs some access to the text they’ll be working with. When reading a text aloud to students, it’s important that it is displayed in a way that all students can easily see it.
7. Intentional Small Group/Partner Work
To support students during independent work time, you can consider small group or partner work. I say “intentional” small group/partner work because it’s important to consider how and why you’re pairing certain students. Pairing two students just because one is a “high” reader and the other is a less sophisticated reader can quickly backfire if you haven’t considered how their personalities/work styles might pair up. Additionally, if you have chosen to provide a small group of students with additional support, just be aware of how much support you’re providing…hopefully not too much! We don’t want to take away all the challenges that a text/lesson presents.
8. Use of First Language
If a student’s first language is available to you, then by all means make use of it as a scaffold. I’m not implying that the whole lesson should be translated. However if you can translate important vocabulary words, make connections between concepts presented, or translate specific instructions then go for it!
As a final note, even if you do not work with ELLs, try to keep in mind that good instruction for second language learners is great instruction for all kids!
Thanks for reading, and download your Scaffolding Strategies Printable for free.
![]()